When it comes to installing or replacing a water heater element, it’s crucial to choose the right one to ensure your heater runs efficiently. But are water heater elements universal?
This question is important to consider, especially if you need to change a corroded or element with sediment buildup.
In this article, we’ll explore the differences between water heater elements to help you make an informed decision.
We’ll cover the types of water heating elements available, how they work, and what you need to know to choose the right one for your electric water heater. So, whether you’re a homeowner or a professional plumber, keep reading to learn more about this important topic.
Key Takeaways
- Choosing the right water heater element is crucial for efficient heating and safety.
- There are different types of water heater elements available. Wrong ones may damage your water heater!
- Understanding how water heater elements work is key to selecting the right one.
Are Water Heater Elements Universal and How They Work?
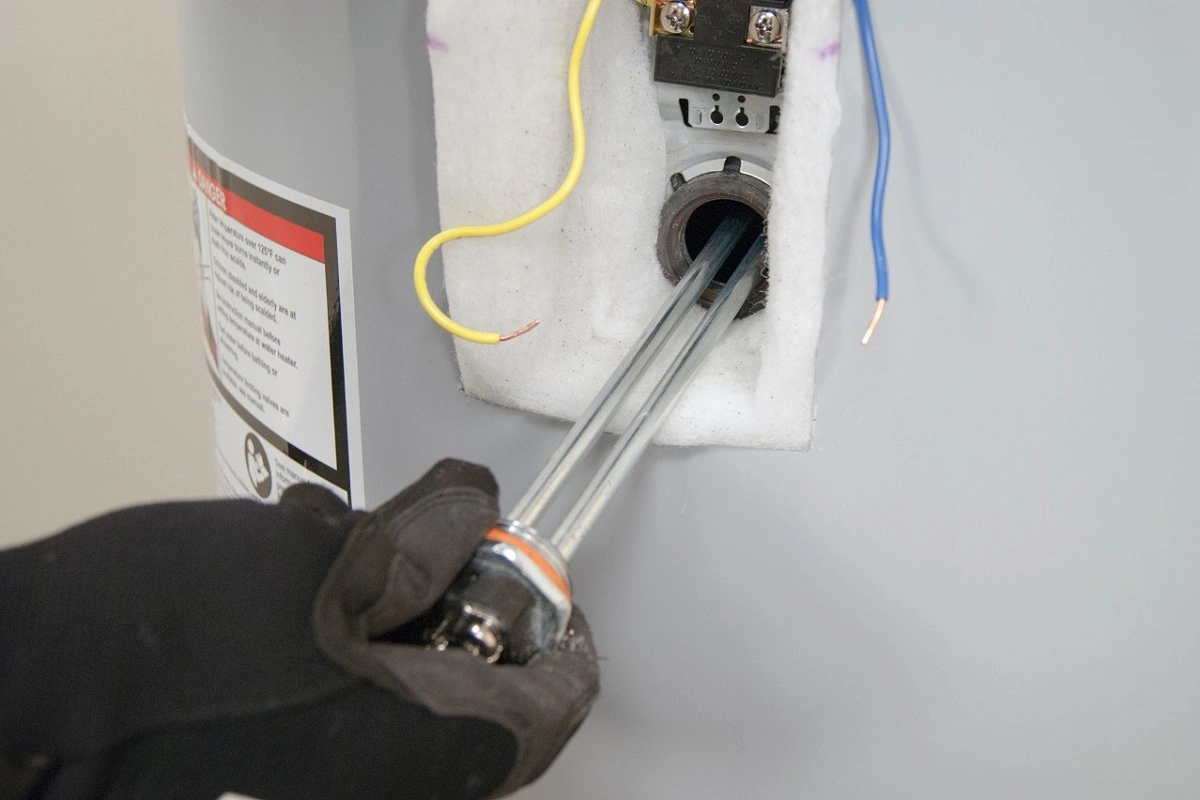

No they are not!
Before getting into details, let’s expain how they work.
In each water heater element, there is a thermostat that measures the temperature of the water. Two separate water heater elements are present in each water heater, and they work separately to heat the water properly.
The top water heating element is the one that turns on first, usually. When it heats the water to a certain temperature, it turns off, and the bottom one turns on. This means that the top and the bottom water heating elements work one at a time, interchangeably.
The heating in an electrical heater occurs when an electric current encounters resistance when passing through an electric element. This results in the heating process.
This cycle repeats only when the heater is full of water, so that the upper element detects cool water. When you shower and use the hot water, the tank will heat up from the bottom. This means that the lower heating element will detect cool water first and start the water heating process. As soon as the upper heating element detects cool water, another heating cycle begins.
A thermostat is a crucial part of each water heating element as it connects to an element. Damaged thermostats result in no hot water in the water heater.
Are Upper and Lower Water Heater Elements The Same?
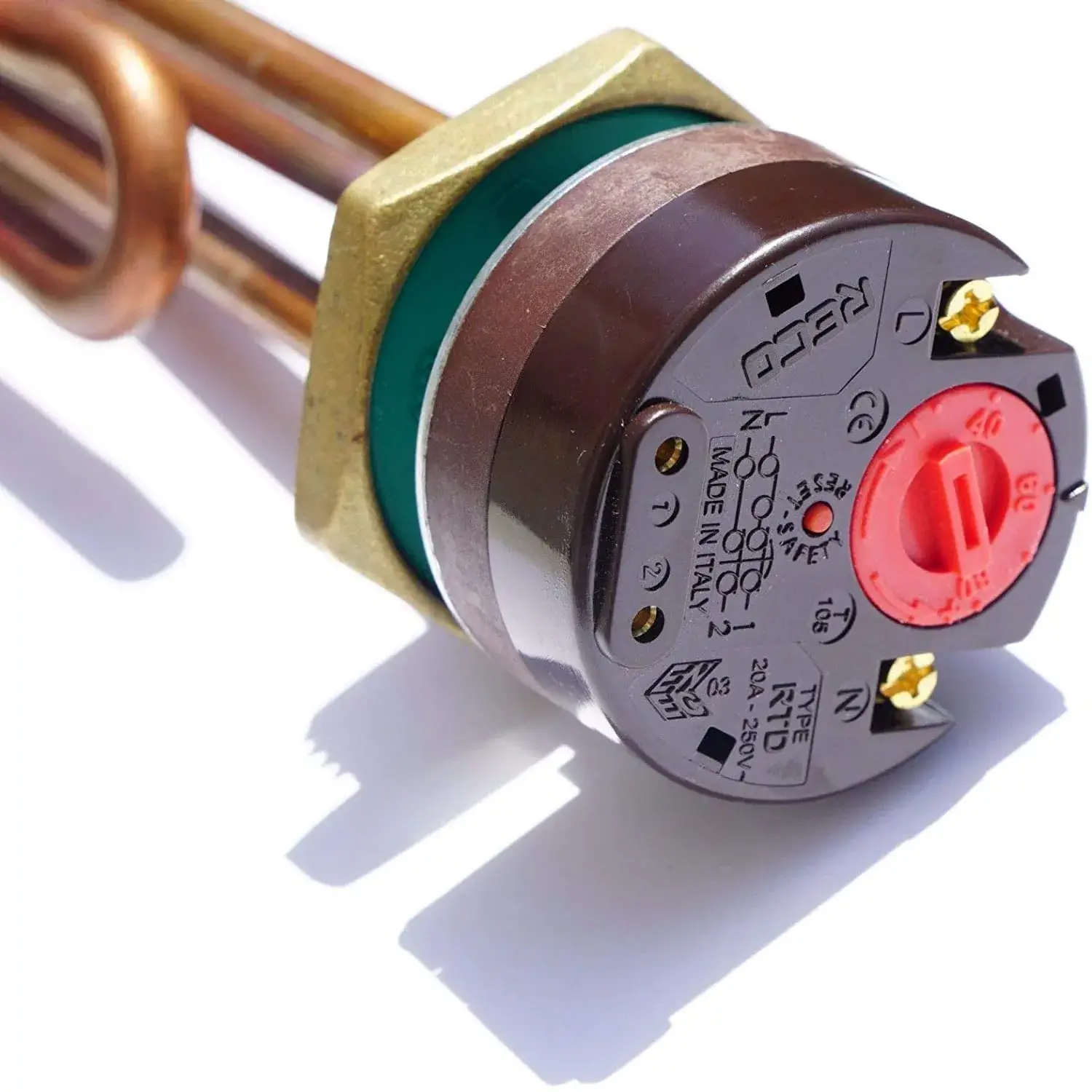
The lower and the bottom water heating elements are identical. If found in the same fixture, they are usually made from the same materials and have the same properties.
However, when replacing them, make sure to research them properly when buying new ones. This is because water heating elements can vary in material, density, wattage, and endurance. If you set the heating elements to the same temperature, the bottom one will always turn on first. In order to always have hot water, it’s useful to set the top heater slightly higher.
In summary, each water heater element contains a thermostat to measure the temperature of the water, and two separate water heater elements work interchangeably to heat the water properly.
The upper heating element turns on first and then turns off when it heats the water to a certain temperature, and the lower heating element turns on when the upper one turns off. Damaged thermostats result in no hot water in the water heater.
What kind of thermostats exist for residental water heaters?
For residential water heaters, the most common types of thermostats are the traditional mechanical thermostats and the more modern digital or electronic thermostats.
Mechanical thermostats use a simple dial or slider for temperature adjustment, while digital or electronic thermostats offer precise temperature control and may include additional features such as programmable settings and diagnostic capabilities
Types of Water Heating Elements

The main types of water heater elements are the screw-in type and the flange type. Screw-in elements are commonly used in residential water heaters, while flange elements are often found in commercial and industrial applications.
Screw-in elements are easier to replace, while flange elements are typically more durable and designed for higher temperature and pressure conditions. Both types come in various materials such as copper, stainless steel, and zinc-plated copper, each offering different levels of corrosion resistance and longevity.
Are Water Heater Elements Universal in Watt Density?
Water heating elements can be classified based on their attachment and the material they are made of. There are different types of attachment styles of water heating elements, including screw-in, bolt-on, and clamp-in. Flange-type and threaded water heating elements are also available. The material of water heating elements can be thick film, ceramic, or metal.
When it comes to the density of the element, we refer to the surface area of the water heating element. The density of elements is interconnected with the wattage, which is sometimes called “watt-density”. Watt density refers to the rating of watts per square inch of surface area. The wattage of most water heater elements can range from 1500 to 5500 watts.
Density of Water Heater Elements
Water heating elements can be classified based on the density of the element. High-density elements are usually made of copper and provide the lowest quality of all three options. They are short-lived as they quickly attract limescale due to constant exposure to extremely high temperatures and hard water.
Also, these types of elements quickly develop corrosion. Low-density elements provide good results in the process of heating, although still not ideal. They are usually made of copper, with a nickel or magnesium oxide coating. These types of elements slow down the buildup of sediments, therefore prolonging their life.
This means they are also less susceptible to corrosion. [1]
Ultra-low density elements are the water heating elements of premium quality. They are usually made from stainless steel of very good quality and provide the best results. This also means that they are least prone to the buildup of limescale or corrosion.
Wattage of Water Heater Elements
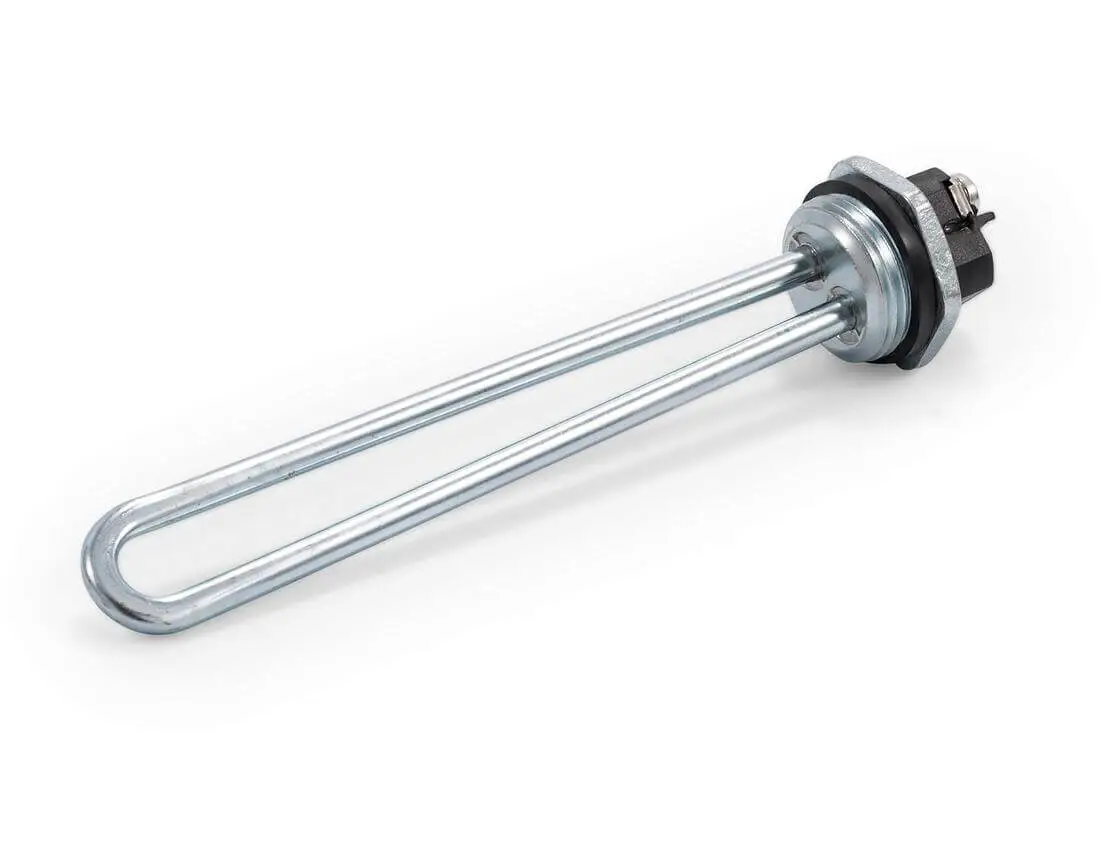

The wattage of water heater elements can range from 1500 to 5500 watts. High-density elements have a high level of wattage per square inch, which is why they get super hot.
In contrast, low-density ones don’t produce the heat that high per square inch, which is why they perform better. It is generally advised to match the voltage and wattage of the new elements.
When buying a new element, keep volts the same, and buy the same or less wattage. Always match the volts of the element to the volts on the heater itself. If you need to replace a 4500-watt heater with a 3800-watt heater, it is totally fine to replace it with a lower wattage, as long as the voltage is the same.
The most common residental water heater element is 4500W/240V element.
In summary, water heating elements can be classified based on their attachment, material, density, and wattage. Different types of attachment styles include screw-in, bolt-on, and clamp-in. Flange-type and threaded water heating elements are also available.
The most common materials of water heater elements are thick film, ceramic, and metal. Watt density refers to the rating of watts per square inch of surface area. The wattage of most water heater elements can range from 1500 to 5500 watts. High-density, low-density, and ultra-low density elements are available. It is generally advised to match the voltage and wattage of the new elements.
The Takeaway
When it comes to water heater elements, it is important to choose the right one for your needs, so that you won’t damage your water heater. There are many differences among them, such as different power and mounting fixtures.
Paying close attention to the wattage and material of the element is crucial. Using a multimeter to perform a continuity test can help determine if the heating element needs to be replaced.
When installing a new element, make sure to follow safety precautions, such as turning off the power supply and draining the tank. Additionally, regularly checking for sediments and ensuring proper water quality can help improve performance and prolong the life of your water heater. [3]
Related: How To Break Sediment Out Of Hot Water Heater
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the wattage of a standard water heater element?
The wattage of a standard water heater element is typically between 1,500 and 5,500 watts. The exact wattage will depend on the size of the water heater and the voltage of the electrical supply.
- How do we determine which water heater element we need?
To determine which water heater element you need, you should first check the manufacturer’s specifications for your particular model of water heater. You should also take note of the wattage and voltage of your current element to ensure that you purchase a compatible replacement.
- Can we replace a water heater element ourselves?
Yes, you can replace a water heater element yourself if you have some basic plumbing and electrical skills. However, if you are not comfortable working with electricity or plumbing, it is best to hire a professional to do the job.
- Are water heater elements interchangeable between brands?
Water heater elements are not always interchangeable between brands. It is important to check the manufacturer’s specifications for your particular model of water heater to ensure that you purchase a compatible replacement element.
- Is it safe to use a higher wattage water heater element?
It is not recommended to use a higher wattage water heater element than what is specified by the manufacturer. Doing so can cause damage to the water heater and potentially create a safety hazard.
- What tools do we need to replace a water heater element?
To replace a water heater element, you will need a few basic tools including a screwdriver, pliers, and a socket wrench. You may also need a voltage tester to ensure that the power is off before you begin working on the water heater.
Read Next: Water Heater Makes Noise When Water Is OFF

Michael Davis is a heating & plumbing expert who currently works as independent contractor in SC. He also writes for Plumbertip.
For almost 10 years he worked on various plumbing tasks across South Carolina.


